What It Means to Streamline a Process
Make your business or organization operate more efficiently by implementing faster or easier processes. It seems like a no-brainer, right? This is the exact purpose of streamlining. Whether your company ships products, onboards new employees, sells virtual technology, or treats medical patients, you can improve overall efficiency by streamlining business processes.
This article will cover the benefits of streamlining, ways to streamline business processes, and approaches to choosing technologies that help you reach that goal.
What Does It Mean to Streamline Something?
Streamlining, by definition, is the act of altering an item to make it simpler or more efficient. For example, you can streamline the work of invoicing clients by ensuring the steps in the process are consistent and repeatable, regardless of who is creating and distributing invoices.
See how Smartsheet can help you be more effective
Watch the demo to see how you can more effectively manage your team, projects, and processes with real-time work management in Smartsheet.
Watch a free demo
What Does It Mean to Streamline a Process?
A business process is a series of repeatable activities that are carried out in specific order to achieve a goal. Each activity constitutes a task. A task, in turn, may be a part of a process, or it may be a one-off event.
For example, in the process of onboarding a new hire, you fill out paperwork, tour the office, provide equipment and work space, and introduce the team members. In this scenario, one of your tasks is to fill out paperwork.
Let's go back to the process of invoicing clients. Documenting this process may be the first step in identifying the activities that contribute to invoicing. Once you've documented your workflow, you may find activities that can be eliminated and/or automated, resulting in a streamlined invoicing process.
What Is Streamlining Business Processes or Operations?
The formality of business processes will vary among organizations. Typically, a formal process is documented, whereas an informal process occurs without much thought or planning. A streamlined business process results in faster outcomes with fewer problems.
Workflow and business process management software solutions are specifically designed to streamline and automate processes across business departments. Numerous business divisions can benefit from streamlined processes:
-
Human resources and administration: New employee onboarding
-
Sales and marketing: Follow-up email distribution
-
Finance and accounting: Vendor invoice submission
-
Operations: Product delivery
-
Procurement: Product orders
-
Management: Employee review
-
IT: Password reset
-
Asset management/predictive maintenance: Asset discovery and inventory
-
Supply chain management: Replenishment of raw materials
-
Compliance documentation: Quarterly reporting
-
Project management: Task notification
Benefits of Streamlining Business Processes
According to a recent Gallup poll, only 32 percent of U.S. workers were engaged in their jobs in 2015. Streamlined business processes not only reduce errors and speed progress, but also help clarify job duties and enforce accountability. Therefore, doing so can improve employee morale and encourage employee engagement.
Businesses of all sizes benefit from streamlined processes. Some additional advantages include the following:
-
Increased efficiency, productivity, agility, and profits
-
Improved communication
-
Clearly documented procedures and greater visibility into processes
-
Reduced errors, holdups, silos, missed deadlines, and redundant work
-
Improved compliance with industry standards
-
Simplified employee training
-
Improved employee adoption
-
Streamlined team coordination
-
Defined task ownership and workflow hierarchy
-
Improved accountability
-
Increased employee morale
-
Established workflow hierarchy and ownership of tasks
-
Enforced accountability
-
Improved customer satisfaction
-
Version control maintained
How to Choose the Business Processes to Streamline
Each organization uses a multitude of business processes every day. Some may be efficient, but others may not be. You can identify these inefficient processes in a number of ways. Unsatisfied customers, increased expenses, and overworked staff are all signs of problematic processes. Other inefficiencies may not be so obvious. A good practice is to take inventory of all business processes, categorize them by department, and prioritize them by importance.
How to Streamline Business Processes
After you have identified and prioritized all business processes, you can begin streamlining. This requires awareness of the process and documentation of each step or activity that takes place to reach the goal. In order to streamline a business process, follow these steps:
-
Identify the goal or end result.
-
Break down the process into discrete steps or tasks.
-
Analyze the process steps, perform value chain analysis, evaluate handoffs, and identify bottlenecks.
-
Gather input from those who perform the process and related tasks, or who benefit from the process.
-
Identify unnecessary activities.
-
Identify redundant activities.
-
Identify activities that can be automated using technology.
-
Redesign/automate tasks.
-
Request resources to deliver on process.
-
Communicate process plan and gain stakeholder/management support.
-
Offer training.
-
Define key performance indicators (KPIs).
-
Track and report on successes and failures.
-
Commit to continuous improvement: test, review, refine.
The size and type of business will help determine the depth of work required when streamlining your processes. For example, a small business may not require stakeholder approval, but a large enterprise will require buy-in from stakeholders and various levels of management.
Streamlining Techniques
Six Sigma, a set of techniques and tools for process improvement, was developed in 1986. Six Sigma continues to be used today, especially in the manufacturing industry, to improve process.
Each business and industry utilizes unique process improvement techniques, but one commonality is that most organizations employ process mapping when working to improve efficiencies. This is also commonly known as a flowchart, a process model, or a workflow diagram. A process map reveals everyone and everything that is involved in a process. The goal of process mapping is to identify areas that the organization can improve.
Below you will find sample business process maps:
-
Flowcharts: Graphical illustrations of your processes.
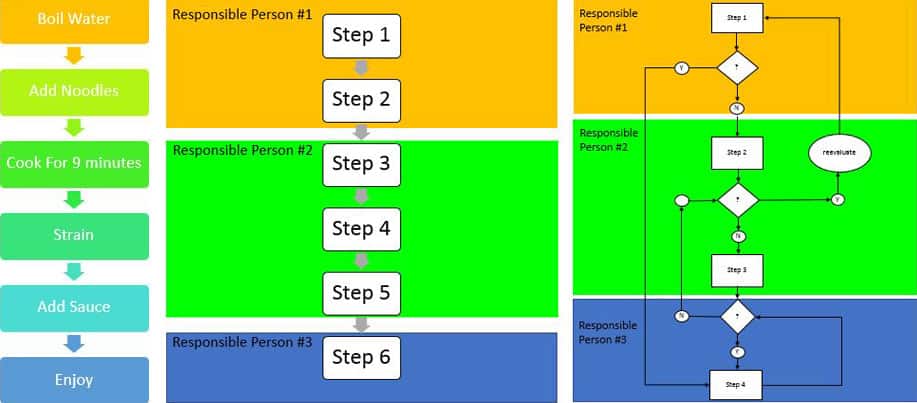
-
Swimlane Diagram: Delineates accountability in a process by placing tasks and activities within the swimlane of the appropriate employee, team, or department.
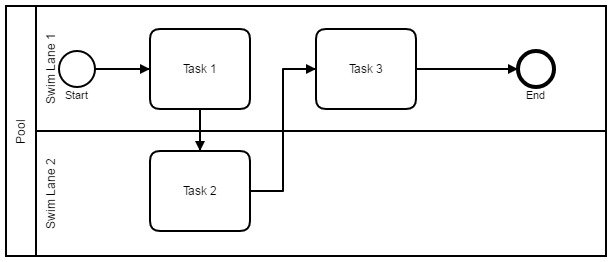
-
Value Stream Mapping: A lean enterprise technique that is used to improve the flow of materials and information in the production of a product or service.
-
SIPOC (suppliers, inputs, process, outputs, customers): A visual overview of a business process.
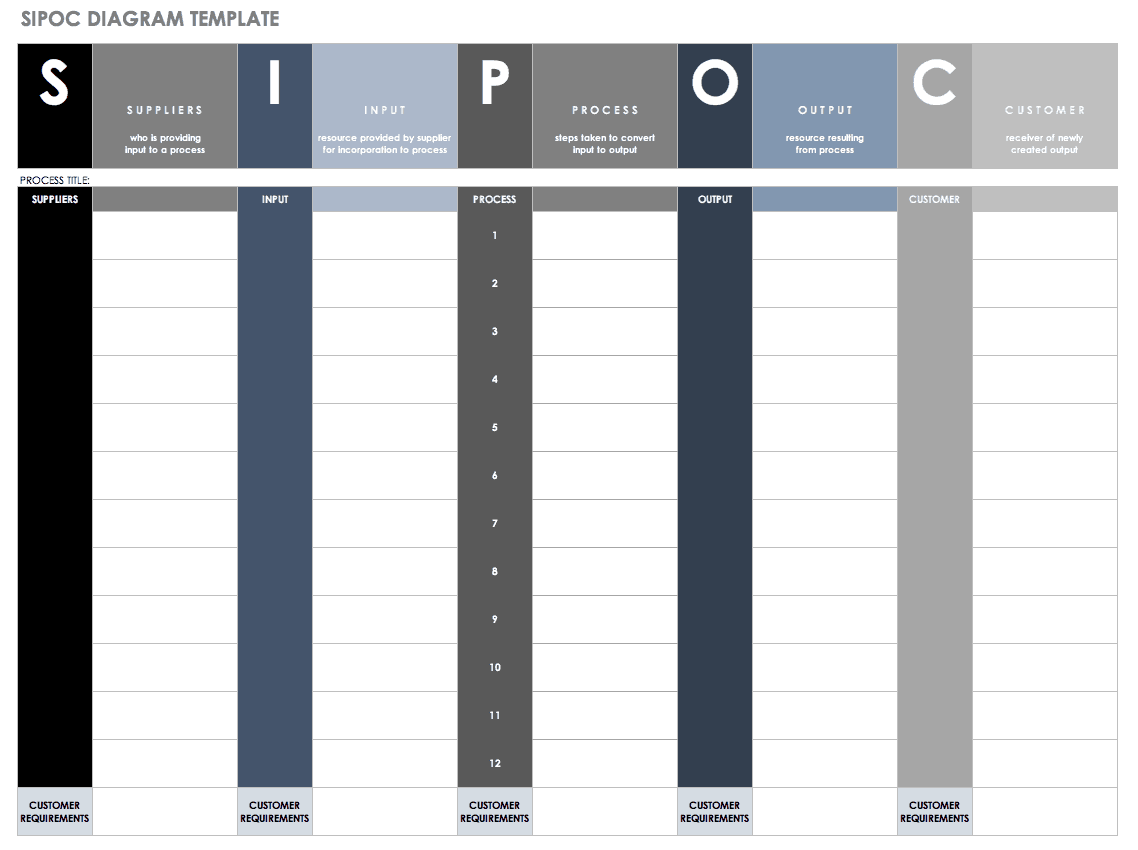
Download SIPOC Diagram Template - Excel
-
Gantt Chart: Used in project management to map project tasks and schedules.
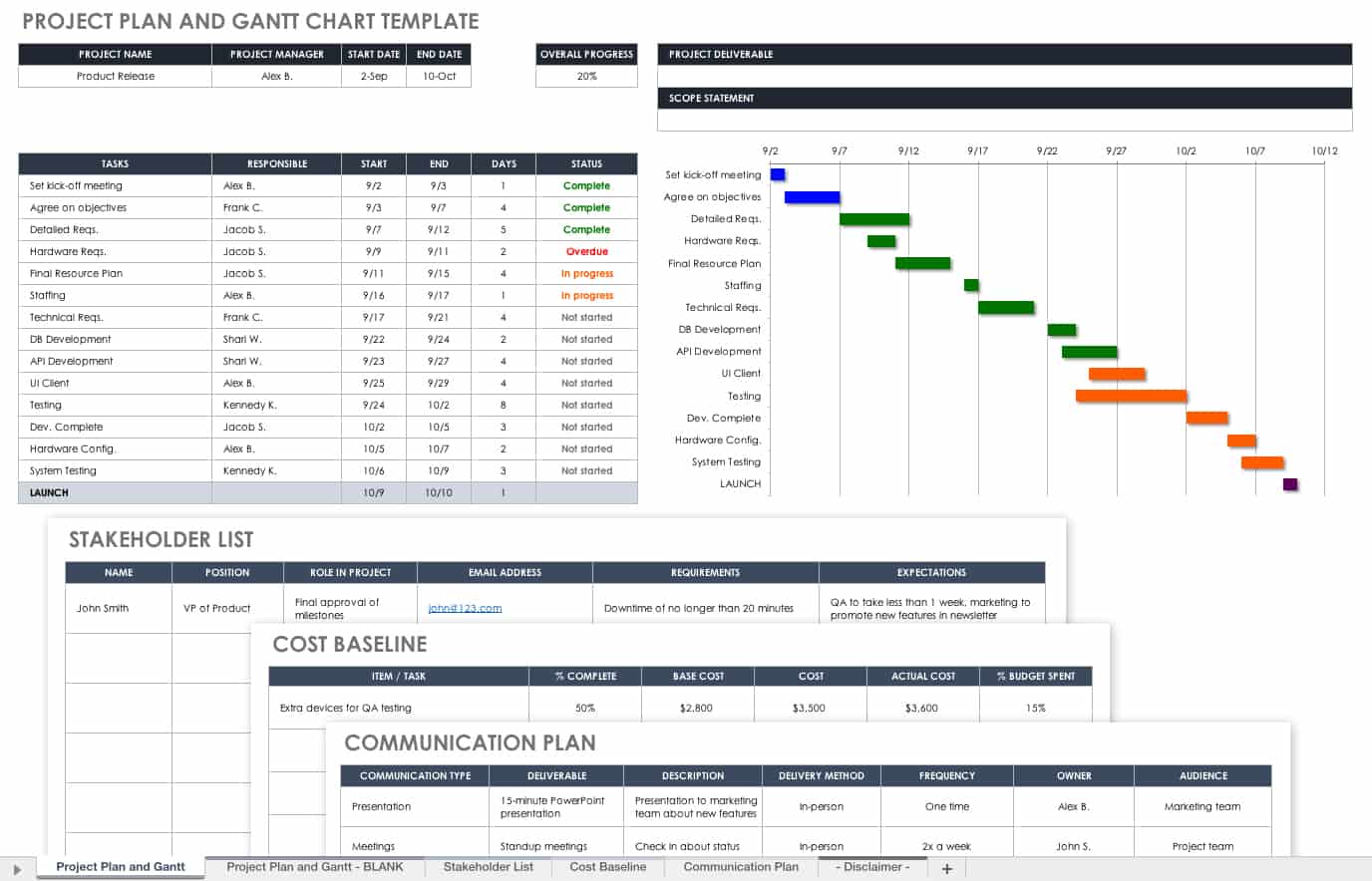
Download Gantt Chart Template
Excel | Smartsheet
Additional techniques used in business process management vary by industry, but may include the following:
-
GUT Matrix
-
BASICS Matrix
-
Root Cause Analysis
-
Systems Diagrams
-
Impact Analysis
-
Risk Analysis
-
Cause and Effect Analysis
-
Value Chain Analysis
-
Fishbone Diagrams
-
Brainstorming
-
Customer Experience Mapping
-
The Change Curve
-
Business Case preparation
-
Kotter's 8-Step Change Model
-
Kaizen
-
Petri-Nets
-
Universal Process Notation
Once you develop the process map, you can begin analysis. This is one of the most important steps in process improvement. Your analysis will uncover real problems that need to be addressed.
Other common philosophies and analysis techniques include the following:
-
Gap analysis
-
Root cause analysis
-
Observation
-
Value chain analysis
-
5 Whys analysis
-
Cause and effect
-
Impact analysis
-
Risk analysis
-
Failure mode and effects analysis (FMEA)
-
Business Process Modeling and Notation (BPMN)
-
Customer experience mapping
-
Lean
-
Total quality management (TQM)
Technologies to Streamline Business Processes
The concept of business process management is closely aligned with TQM, continual improvement, Six Sigma, and Lean process improvement approaches. Business process management has become big business for software vendors, who have developed a multitude of innovative solutions to streamline workflow or business processes.
These tools are designed to collect, automate, measure, and improve business processes. Below you will find information about a variety of business/workflow process automation software.
-
Business Process Management (BPM) Software: Business process management as an operations management discipline views business processes as important assets that must be managed and clearly developed in order to deliver value. BPM software helps organizations automate and optimize business processes. According to Gartner Peer Insights, "A BPM platform minimally includes: a graphical business process modeling capability, a process repository to handle the modeling metadata, a process execution engine and a state management or rule engine." Digital transformation initiatives rely on the intelligence, rapid application development, and mobile capabilities of modern BPM solutions to fulfill the demand for agility and speed.
-
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Software: CRM solutions are focused on the organization's interactions with customers and prospects. Process efficiency is extremely important, with the goal of improving relationships with the customer.
-
Enterprise Content Management (ECM)/Enterprise Document Management Software: ECM solutions are used to manage, store, preserve, and deliver content to processes across an organization. ECM software works closely with BPM and CRM solutions.
-
Project Management Software: Also referred to as flowchart software, project management solutions help take unwieldy projects and organize them into processes.
-
Product Management and Development Software: Product development software follows a process that takes a product or service from conception to market-readiness.
-
Legal, Accounting, and Finance Tools: Software solutions designed for legal and finance can help streamline document signing and tracking, invoicing, expense reporting, payroll, bookkeeping, taxes, reporting, and analytics.
-
Human Resources and Marketing Software: These tools can simplify the hiring process, employee scheduling, timesheet approvals, customer feedback, customer engagement, and collaboration.
-
Personal Productivity Tools and Apps: Apps and online solutions are readily available for automating the creation of checklists, managing to-dos, logging activities, and tracking time spent.
What to Look for in Business Process Modeling Tools
Business process modeling is one element of business process management. The goal of business process modeling is to benchmark current processes with future goals. Visual documentation helps users understand and analyze the activities, events, and resources associated with a process. Business process modeling incorporates process mapping, process discovery, and process simulation.
When evaluating business process modeling tools, consider the following criteria:
-
Easy for business departments to learn
-
Easy for IT teams to discuss with and teach to other departments
-
Inexpensive and industry compliant
-
Includes an integrated workflow editor tool with graphic interface
-
Ability to simulate workflow before implementing
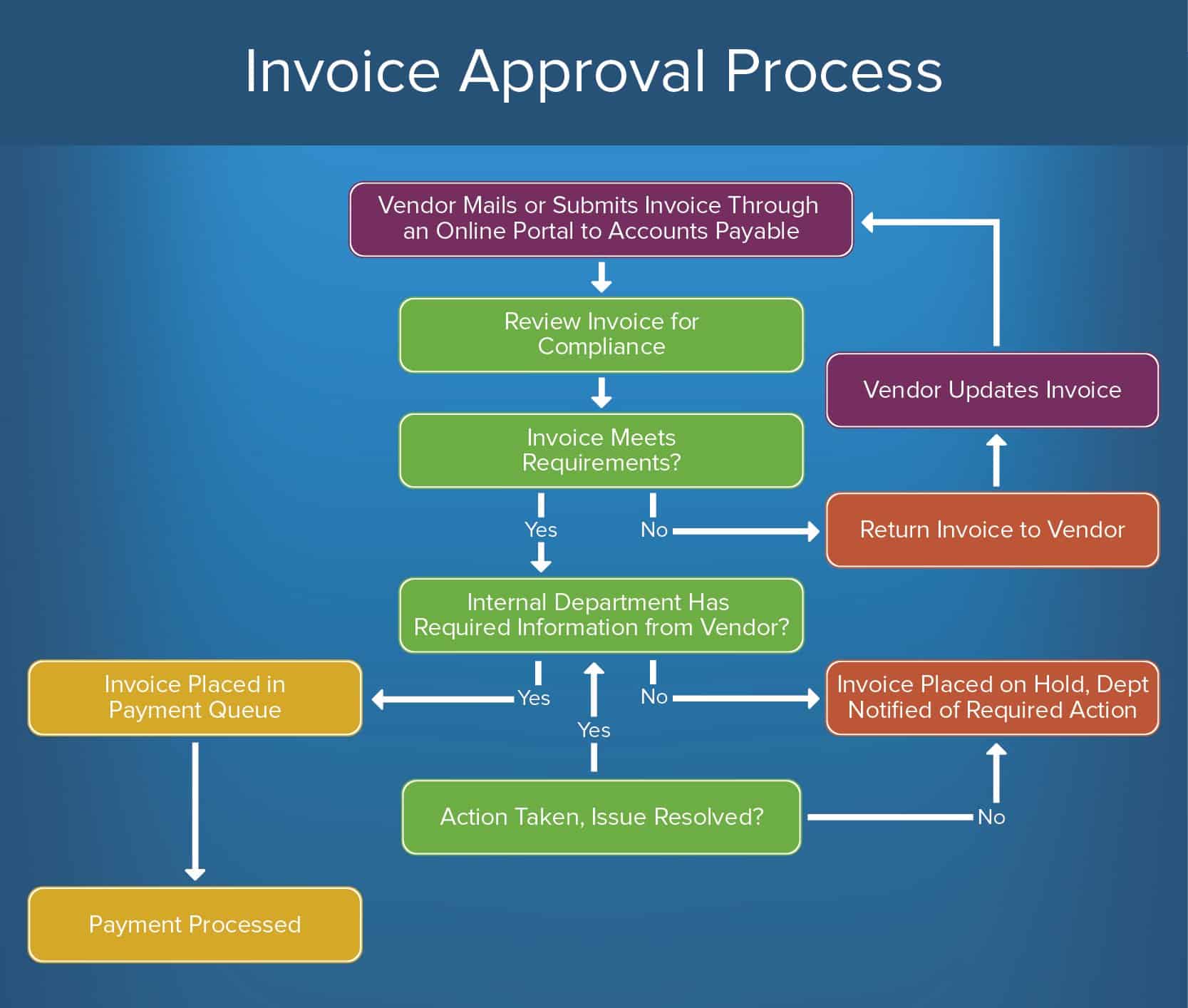
Sample Automated Workflow Process
Invoice approval, employee onboarding, expense processing, and service requests are just a few examples of work processes that businesses can automate.
Invoice submission is a common practice across all industries, and can be streamlined with automation. Vendors, contractors, and employees submit invoices on a regular basis. Create a repeatable approval process to ensure everyone is paid quickly and accurately
Signs It's Time to Update Your Business Technology
There's more than one way to streamline your business processes. In some cases, simply updating your company's technology can yield greater efficiency and higher productivity. The following list includes indicators that you might need to enact an improvement plan:
-
Slow server/network
-
Employees complain about poor IT support
-
Employees complain that they don't have the tools they need for the job
-
Employees express dislike for the solutions you have and have stopped using them
-
Silos exist between departments and data is not unified
-
Technology doesn't allow your business to be agile/doesn't evolve with your business
-
The customer experience is lacking
Best Practices for Business Automation
The decision to streamline your business processes is important. If your business processes are causing customer dissatisfaction or employee discontent, or if they cost you more than necessary, it's time to make a change. Below are a few tips that will help improve business operations with automation:
-
Find out what your customers think by conducting a survey. Target questions to find out what is and isn't working.
-
If employee training is necessary, hire an outside expert who has experience training numerous types of people and different levels of leadership. Consider specific training for leaders. Consider the impact of downtime due to staff attending training (this is especially important for smaller businesses).
-
Identify broken processes and focus on fixing them before applying technology. As Bill Gates is famously said, "The first rule of any technology used in a business is that automation applied to an efficient operation will magnify the efficiency."
-
Identify whether general staff or programers will use and/or manage any technology solution.
-
Ensure you will see a return on your investment in any technology you purchase.
-
Consider the 80/20 rule or Pareto principle as you work on efficiency. For example, fixing the top 20 percent of inefficient processes may improve 80 percent of your process problems.
-
Evaluate vendor-delivered, cloud-based solutions that are agile, extendable, mobile-friendly, and configurable to your specific needs.
Glossary of Terms
Streamlining: The process of making an organization of system more efficient by implementing simple and more agile approaches.
Task: A single piece of work that needs to be completed.
Process(es): A series of tasks or activities that need to be completed in order to meet an end goal.
Business Processes: A series of tasks or activities that are used in a business environment and need to be completed in order to meet an end goal.
- Informal Business Processes: A process that occurs without much thought or planning.
- Formal Business Processes: A process that is documented.
Workflow: A sequence of processes that take work from commencement to completion.
Documentation: Materials available online, on paper, or on digital or analog media that include information or data.
Business Process Management (BPM): An operations management discipline that views business processes as an important asset that must be managed and clearly developed in order to deliver value.
Business Process Management (BPM) Strategy: An approach to identifying, designing, implementing, analyzing, monitoring, regulating, and improving business processes.
Business Process Automation: The act of using technology to automate business processes.
Business Process Improvement: The act of analyzing and improving business processes. This may include automating, eliminating steps, adding tasks, or eradicating a process all together.
Quality Assurance (in process automation): Testing each stage of a process to ensure the desired level of effectiveness is achieved.
Business Process Mapping: Identifying everyone and everything involved in a process. The goal of process mapping is to identify areas that can be improved.
Business Process Modeling: The act of benchmarking current processes with future goals. Visual documentation is used to clearly understand and analyze the activities, events, and resources associated with a process. Business process modeling incorporates process mapping, process discovery, and process simulation.
Business Process Modeling and Notation (BPMN): A standard for business process modeling that diagrams a process in graphical form.
Business Process Reengineering (BPR): A strategy that focuses on analyzing, designing, and restructuring business processes to dramatically improve operations.
Digital Transformation: The transformation of organizational activities to leverage digital technology opportunities in all areas of business.
Get the Most Out of Your Business Processes and Workflows with Smartsheet
Empower your people to go above and beyond with a flexible platform designed to match the needs of your team — and adapt as those needs change.
The Smartsheet platform makes it easy to plan, capture, manage, and report on work from anywhere, helping your team be more effective and get more done. Report on key metrics and get real-time visibility into work as it happens with roll-up reports, dashboards, and automated workflows built to keep your team connected and informed.
When teams have clarity into the work getting done, there's no telling how much more they can accomplish in the same amount of time. Try Smartsheet for free, today.
What It Means to Streamline a Process
Source: https://www.smartsheet.com/streamlining-processes
0 Response to "What It Means to Streamline a Process"
Post a Comment